Crypto
bitcoin, blockchain, blockchain scalability, censorship resistance, crypto governance, cryptocurrencies, cryptocurrency benefits, decentralization, Decentralized Finance, DeFi, Ethereum, financial empowerment, peer-to-peer network, privacy, security, Smart contracts, transparency
Kayztr
0 Comments
The Importance of Decentralization in Cryptocurrencies
Introduction
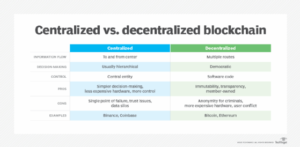
Decentralization is a fundamental principle that underpins the entire concept of cryptocurrencies. Unlike traditional financial systems, which are centralized and controlled by a single entity, decentralized cryptocurrencies operate on a peer-to-peer network, distributing power and control among all participants. This article explores the importance of decentralization in cryptocurrencies and its implications for the future of finance.
What is Decentralization?
Decentralization refers to the distribution of power away from a central authority. In the context of cryptocurrencies, it means that no single entity, such as a government or financial institution, has control over the entire network. Instead, control is spread across a vast number of nodes (computers) that participate in the blockchain network.

Key Benefits of Decentralization
Enhanced Security
Decentralized networks are inherently more secure than centralized ones. Since there is no central point of failure, it is much harder for malicious actors to launch attacks. Even if one node is compromised, the rest of the network remains unaffected, ensuring the integrity and security of the data.
Increased Transparency
In a decentralized network, all transactions are recorded on a public ledger known as the blockchain. This transparency ensures that all participants can verify transactions independently, reducing the risk of fraud and manipulation. It fosters trust among users and ensures accountability.
Greater Privacy
Decentralization allows users to maintain their privacy. Unlike centralized systems, where user data is stored on central servers, decentralized systems do not require users to reveal personal information to a single entity. This ensures that users retain control over their data.
Censorship Resistance
One of the most significant advantages of decentralization is its resistance to censorship. Since there is no central authority controlling the network, it is nearly impossible for any single entity to censor or block transactions. This is particularly important in regions with restrictive governments or unstable economies.
Empowerment of Individuals
Decentralization empowers individuals by giving them control over their financial transactions. It removes the need for intermediaries, such as banks or payment processors, allowing users to transact directly with one another. This not only reduces costs but also speeds up transactions and makes financial services more accessible.
Real-World Examples
Bitcoin
Bitcoin is the most well-known example of a decentralized cryptocurrency. It operates on a peer-to-peer network, where transactions are verified by network nodes through cryptography and recorded on a public ledger. This decentralization ensures that no single entity can control or manipulate the Bitcoin network.
Ethereum
Ethereum takes decentralization a step further by enabling decentralized applications (dApps) to run on its blockchain. This allows developers to create and deploy smart contracts that operate without the need for a central authority, opening up a world of possibilities for decentralized finance (DeFi), gaming, and more.
Use this code in Criptolia to claim article reward: CENTRALBLOCK
Challenges of Decentralization
Scalability
One of the primary challenges of decentralization is scalability. Decentralized networks can struggle to handle a large number of transactions simultaneously, leading to slower processing times and higher fees. However, ongoing research and development aim to address these issues through innovations such as sharding and layer-2 solutions.
Governance
Decentralized systems can also face challenges related to governance. Without a central authority, reaching consensus on network upgrades and changes can be difficult. This often requires extensive coordination and collaboration among participants, which can be time-consuming.
Conclusion
Decentralization is a cornerstone of cryptocurrencies, providing enhanced security, transparency, privacy, and resistance to censorship. While there are challenges to overcome, the benefits of decentralization are profound and far-reaching. As technology continues to evolve, decentralized systems have the potential to transform the way we conduct financial transactions, empowering individuals and fostering a more open and inclusive financial ecosystem.


Post Comment